Hovering over an image will enlarge it and point out features (works better on desktop than on mobile).
![]() A camera indicates there are pictures.
A camera indicates there are pictures.
![]() A speaker indicates that a botanical name is pronounced.
A speaker indicates that a botanical name is pronounced.
![]() A plus sign after a Latin name indicates that the species is further divided into varieties or subspecies.
A plus sign after a Latin name indicates that the species is further divided into varieties or subspecies.
Most habitat and range descriptions were obtained from Weakley's Flora.
Your search found 4 taxa in the family Myrsinaceae, Myrsine family, as understood by PLANTS National Database.
![]()
![]() Common Name:
Coral Ardisia, Hen's Eyes, Coralberry, Marlberry
Common Name:
Coral Ardisia, Hen's Eyes, Coralberry, Marlberry
Weakley's Flora: (4/14/23) Ardisia crenata FAMILY: Primulaceae
SYNONYMOUS WITH PLANTS National Database: Ardisia crenata FAMILY: Myrsinaceae
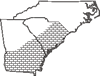
Habitat: Moist suburban forests, floodplains, mesic flatwoods, moist forests
Uncommon in GA, rare in SC
Non-native: Asia
Common Name: Japanese Ardisia, Marlberry
Weakley's Flora: (4/14/23) Ardisia japonica FAMILY: Primulaceae
SYNONYMOUS WITH PLANTS National Database: Ardisia japonica FAMILY: Myrsinaceae
Habitat: Disturbed areas
Non-native: Asia

Common Name: Shoebutton Ardisia
Weakley's Flora: (4/14/23) Ardisia elliptica FAMILY: Primulaceae
SYNONYMOUS WITH PLANTS National Database: Ardisia elliptica FAMILY: Myrsinaceae
Habitat: Hammocks, suburban woodlands
Non-native: Asia

Common Name: China-shrub
Weakley's Flora: (4/14/23) Ardisia solanacea FAMILY: Primulaceae
SYNONYMOUS WITH PLANTS National Database: Ardisia solanacea FAMILY: Myrsinaceae
Habitat: Disturbed hammocks
Non-native: Asia
Your search found 4 taxa. You are on page PAGE 1 out of 1 pages.




