Fruit
adapted from Woody Plants of the Blue Ridge by Ron Lance. Used by permission.
To see photographic examples of a term, click the camera next to it in the list of botanical terms.
One fruit contains the seed (which holds the matured ovule), and any coverings derived from the ovary wall or other flower parts.
Seeds may be single per fruit (then often called "pits" or "stones"), or numerous.
Flesh of the fruit may be pulpy, soft and juicy, or hardened or leathery.
Arils are appendages which may surround the seed, as in bittersweet, or resemble an ovary in some gymnosperms like yew and ginkgo.
Simple vs. Compound:
Simple fruits come from one pistil in one flower.
Compound fruits come from more than one pistil in one flower — or — from close clusters of flowers in an inflorescence.
- Aggregates are compound fruits from one flower which had many pistils, as in maple, magnolia, rose, blackberry.
- Multiples are compound fruits from inflorescences, usually from closely clustered heads or spikes of flowers, crowding and growing together as one mass with maturity (as in mulberry, osage-orange, sweetgum, sycamore).
Fruit types:
Drupe: usually 1-seeded; endocarp stony; matured ovary wall fleshy (as in cherry, blackgum)
Berry: from one ovary, with several immersed seed (as in blueberry, pawpaw)
Pome: from one ovary with fused carpels, the "skin" derived from a hypanthium which covered ovary (as in apple, servicebeny)
Hip: in roses, an aggregate of achenes, surrounded by a fleshy-walled receptacle
Achene: from a simple pistil; a small, hard fruit with a thin pericarp or seed coat; as in sycamore, rose, sweetshrub "seeds"
Samara: a winged achene-like fruit, as in maple, ash
Nut: a hard, generally 1-seeded fruit partially or wholly enclosed in a husk (involucre), as in hickory, chestnut, oak
Legume: a one-chambered fruit from a simple pistil; splits down two sutures; in Fabaceae (legume) family
Pod (follicle): a one-chambered fruit from a simple pistil; splits down one side, as in magnolia, yellowroot
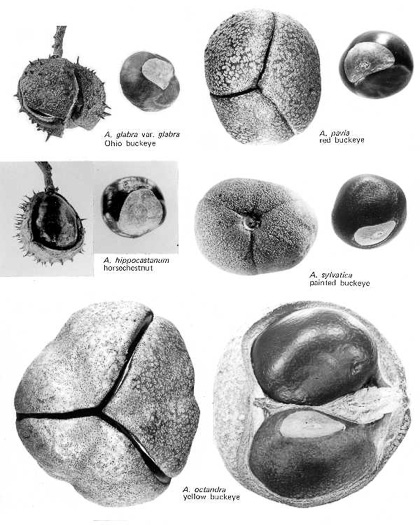
Capsule: usually several-chambered fruit; from a compound pistil; splits along 2 or more sutures, as in rhododendron, buckeye
Strobile: a conelike fruit derived from a spike or catkin-like inflorescence; composed of nutlets growing between protective layers of bracts; in birches and alders
Cone: the fruit of gymnosperms such as pine, spruce; the seeds are matured ovules held between bracts, not in ovaries